Wi-Fi RF Spectrum; interferences; how to detect them, case study: microwave oven.
Table of Contents
Detect wifi interferences helps us to improve wifi speed
To detect wifi interferences and learn why it occurs and how to avoid it is important to improve and solve wifi network speed problems.
The Wi-Fi standard operates in two frequency ranges. The most widely used RF spectrum within the 2.4GHz range is commonly affected by many different wireless interferences and noise sources.
Among these sources, microwave ovens are one of the most common, which are present in most households, offices and factories, usually located in kitchens/buffet areas.
Wi-Fi (802.11) interferences.
Most common noise and interference sources:
- Microwave ovens.
- Wi-Fi surveillance video cameras.
- Wireless telephones and microphones.
- Wireless baby monitors.
Microwave ovens, just like wireless technologies such as Wi-Fi, use electromagnetic waves.
They emit electromagnetic waves in the microwave range, from 0.3GHz, UHF (Ultra-High frequency) to 300GHz, EHF (Extremely-high frequency), normally in the 30-300GHz range
This is done by exciting the water particles and changing their orientation millions of times per second, and that increased friction between the molecules results in heat.
Since most foods have a large water content, this is a quick and easy way too heat up and cook them.
The electromagnetic microwave frequency range is very wide, the problem lies in that the frequency of these waves, in the case of microwave ovens, is approximately 2.45GHz, operating at 500 to 1,100 Watts of power.
Coexistence in the radio spectrum range
Since these waves use the same radioelectric spectrum, Wi-Fi transmissions have to share the RF medium with magnetron-emitted microwaves, and since Wi-Fi data packets should be consistently received by the client devices, when the transmission is disrupted by external sources, the data rate is degraded, which does not allow a correct data reception by the client devices, since the interference or noise range prevent the data packets to be properly reconstructed.
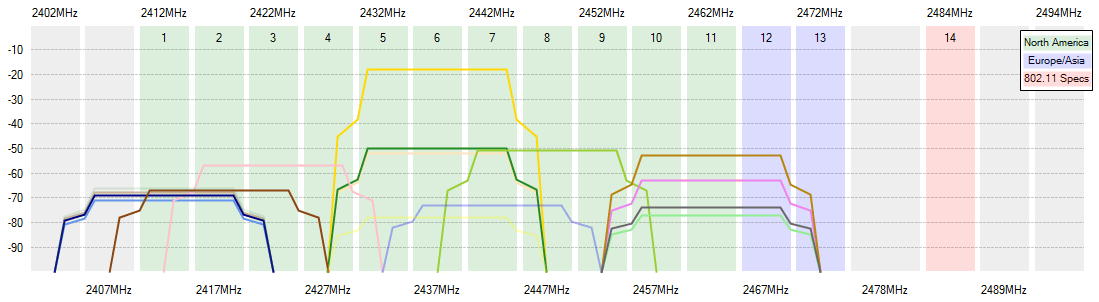
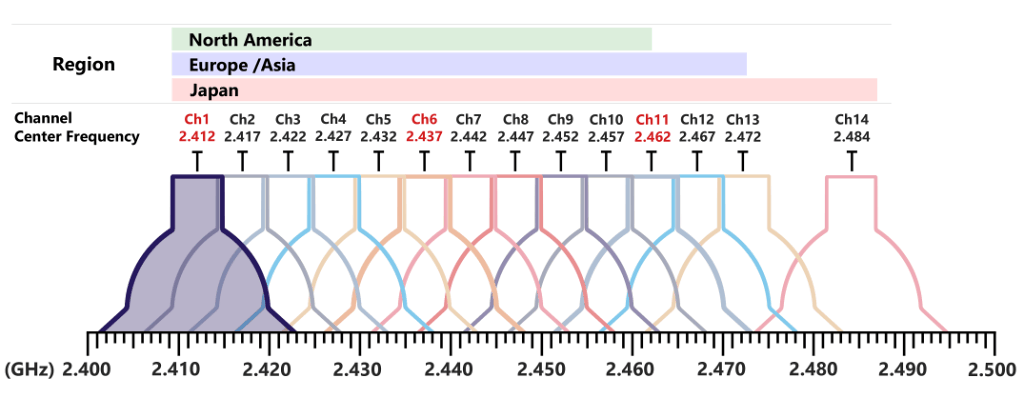
To transmit data wirelessly within the radioelectric spectrum, precisely on the 2.4GHz frequency, transmissions may range approximately from 2.4 to 2.5GHz.
This range within the radioelectrical spectrum is also affected by local legislations, allowing different ranges according to the country.
How a Microwave Oven Works
A brand new microwave oven should be properly insulated and should comply with all local radioelectric emissions laws and regulation for the target market, as well as the regulations and standards from international regulatory agencies.
Agencies such as the International Electronics Commission (IEC), the International Committee on Electromagnetic Safety (ICES) of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC).
Technological challenges.
That is to say that once its door is shut and in operation, the electromagnetic emissions that heat up the food contained inside should not escape the oven.
Which internals acts much like a Faraday cage, causing the emissions to bounce inside the confined area to heat up the food more efficiently.
Have you ever wonder why microwave heated food is hotter on the outside and cooler on the inside, and sometimes, when you are trying to heat a small piece, it barely gets warm?
This is due to the wave emitter, the magnetron, always emit waves at the same incidence angles, so they always bounce on the same places.
How it solves challenges.
To prevent that, an helix should be included to make the waves bounce in all possible directions, as well as a rotating plate, which increase the incidence area.
When the rays hit the surface of the food, they lose power as they go into the food, so that explains why the food is hotter on the outside than on the inside.
Although this explanation does not apply to Wi-Fi technology and on how to detect wifi interferences, it is interesting to know how the electromagnetic waves are emitted, why they are forced to bounce, and what happens when a microwave oven in not properly insulated or allows for a radiation leakage.
![]()
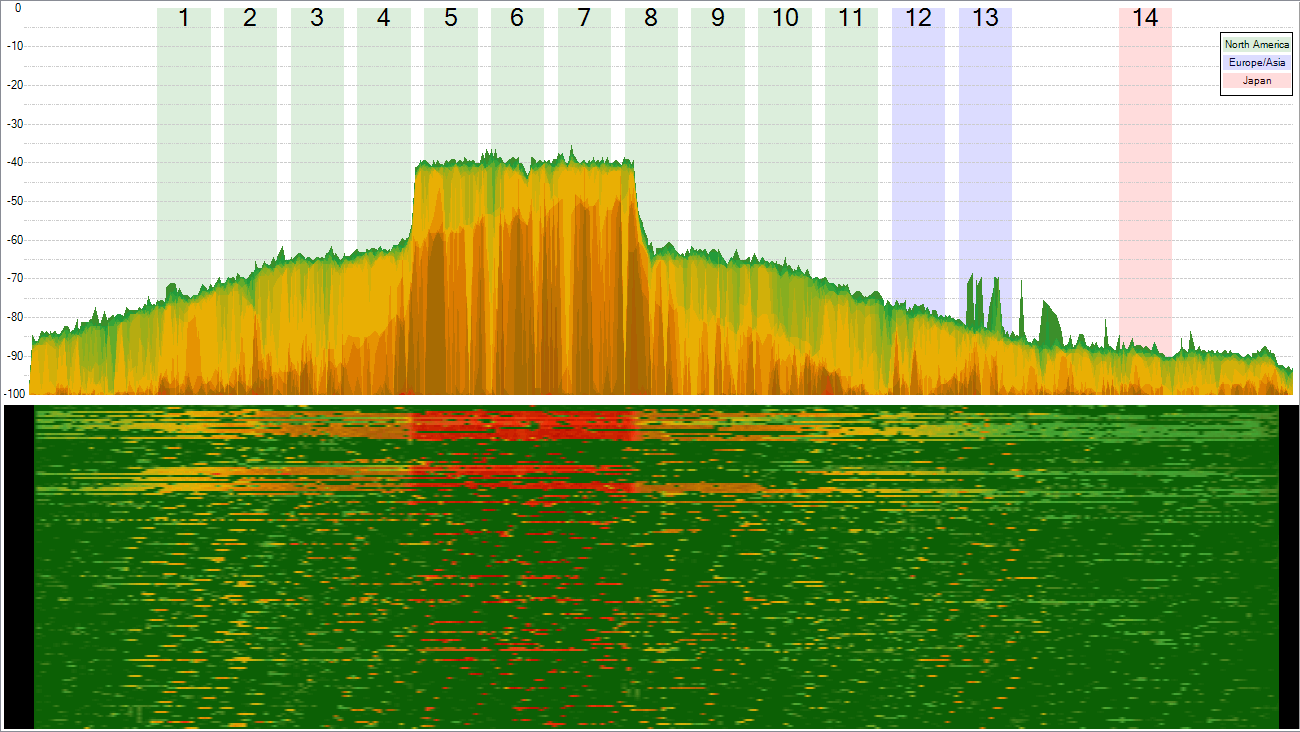
How the 2.4GHz Radioelectrical Spectrum Looks Like.
As the image shows, we have a normal 2.4GHz spectrum, with a few operating Wi-Fi networks and their typical transmission pattens, where you can observe the channel hopping to broadcast their networks through management beacon packets, some more intense data transmission peaks, yet nothing out of the ordinary.
Microwave ovens are not perfect, and certain amount of energy, namely waves, leak out to the exterior, and when these waves are on the Wi-Fi frequency band of 2.45GHz, they interfere with data transmissions on the same frequency range, from channel 8 on.
How are the and how to detect wifi interferences produced by a microwave.
In this new image of the spectrum, you can observe a new pattern with higher intensity and bandwidth than an announcing access point would have, and this is caused by an interfering microwave oven.
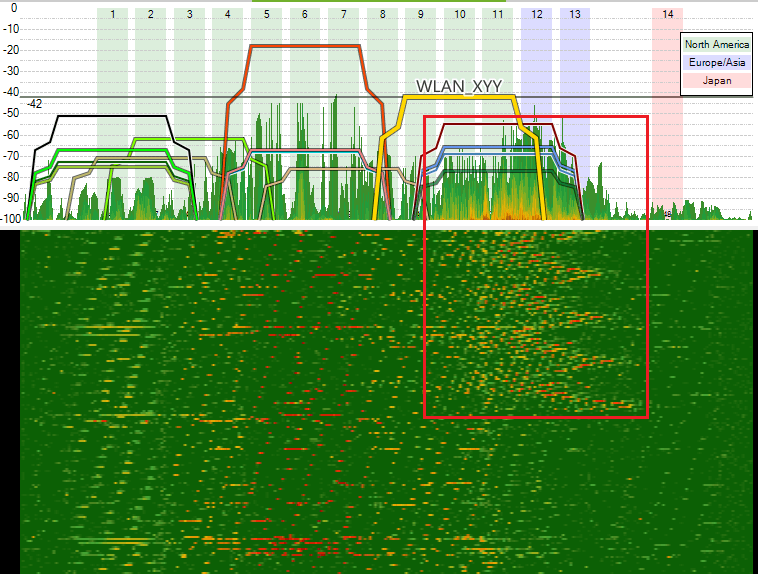
Normally, an access point operating on channel 8 or higher, will hardly maintain service with acceptable values, and it could even experience service interruptions while the microwave oven is in operation.
Most common reasons
For home networks, this could cause intermittent service disruption, and for SOHO (Small Office/Home Office) environments with a coffee machine and a microwave oven, this could be a problem.
Ssince a microwave oven located close to an operating access point could probably degrade the data transmission and communications quality, and possible disrupt the service in occasions.
For large companies, shopping malls, or hotels, where a large number of kitchen areas coexist, and client/host/employee networks are normally deployed, this could be a big problem.
Its a huge challenge when trying to identify the cause of connectivity and network performance issues.
In case you would like to perform a full site survey, it is also recommended to perform radioelectric spectrum measurements.
This will help us identify interference and noise sources that are transmitting in the Wi-Fi range, such as other Wi-Fi devices or wave emitting devices or appliances.
Once this sources are successfully identified, the spotted areas can be filtered out from the network’s inventoried access points, to focus on these external interference sources.
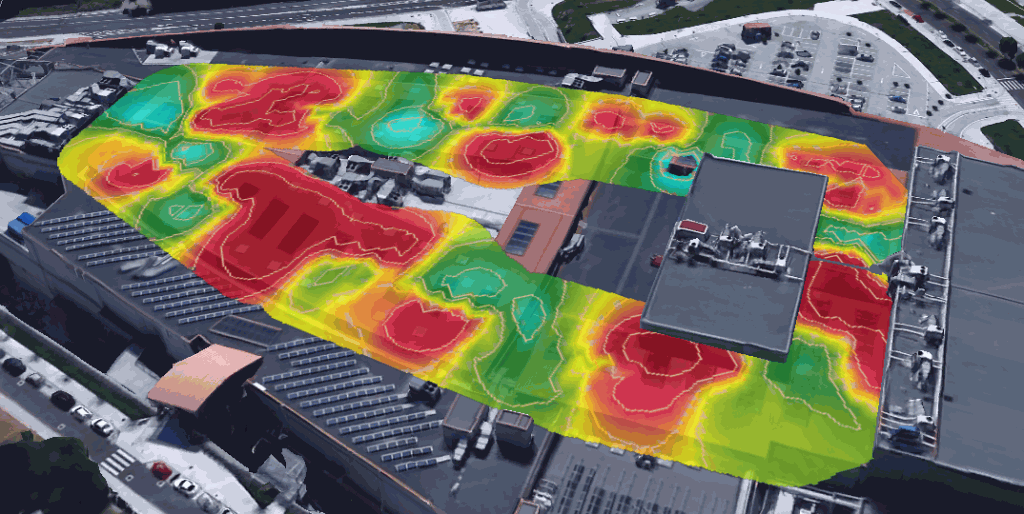
Conclusions on why to detect wifi interferences is important
As we have seen, it is important to acknowledge non-Wi-Fi emissions in the radioelectric spectrum and to detect wifi interferences in order to identify possible network performance issues.
Bbesides focusing on access point configuration parameters or network coverage levels.
A correct parametrization, an appropriate channel setting, and a perfect coverage do not mean anything when an interfering emission source comes into play without being detected by a conventional passive or active site survey.
Try Acrylic Wi-Fi Heatmaps NOW to analyze your Wi-Fi network
This article is part of a series of articles about WiFi radio frequency spectrum analysis
- Wi-Fi RF Spectrum; interferences; how to detect them, case study: microwave oven.
- Wi-Fi RF spectrum, baby monitors, wireless cameras, interference and noise
- Wi-Fi Spectrum Analysis, How to Perform One, and What Information It Provides